Signs of a Happy Dog
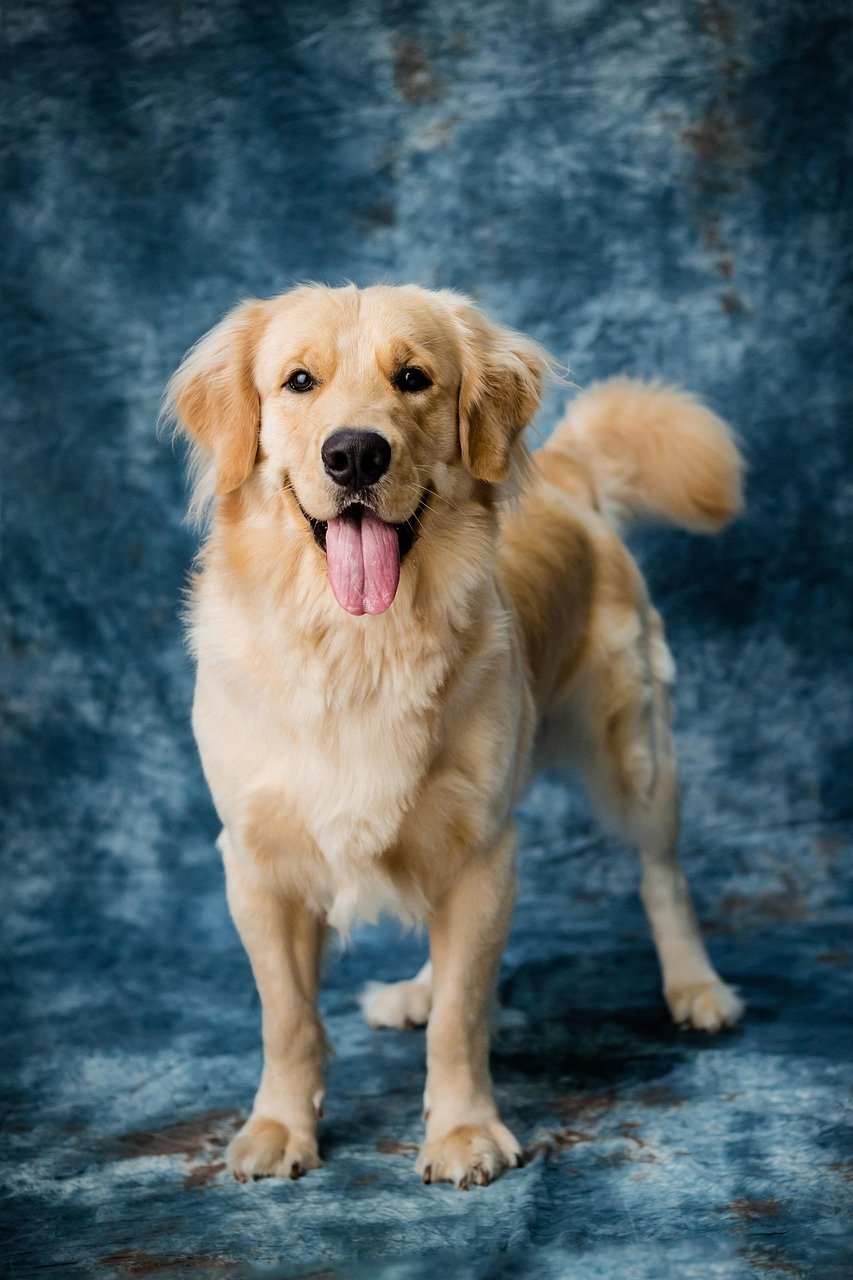
Understanding canine emotions is crucial for any dog owner, as it allows for a stronger bond and better care. One key aspect of recognizing a happy dog is observing their body language and behaviors. A primary indicator of joy in dogs is a wagging tail, which often varies in motion and speed depending on the dog’s excitement level. A tail that wags at a high rate is typically a sign of happiness, with the tail positioned above the dog’s back in a relaxed manner. Conversely, a low or stiff tail may indicate anxiety or discomfort.
Another hallmark of a happy dog is a playful demeanor. This can manifest through playful barks, pouncing, and a general eagerness to engage in various activities such as fetching a ball or playing tug-of-war. Dogs will often display the play bow, where they lower their front legs while keeping their rear elevated, signaling a desire to play. This behavior reflects both their mental and emotional well-being, and a playful dog often invites interaction, whether with humans or other animals.
Moreover, a happy dog typically exhibits a relaxed body posture. When a dog feels secure and content, it may rest comfortably with its body loose, ears in a natural position, and mouth slightly open, sometimes even panting gently. This contrasts sharply with behaviors indicative of stress, such as cowering or tucking their tail. Additionally, a happy dog often engages warmly with people and pets, showing friendliness through sniffing, wagging, or even initiating playtime.
Overall, the signs of a happy dog encapsulate an array of physical gestures and social activities. Owners who understand these behaviors can foster a positive environment that enhances their dog’s well-being while ensuring their emotional needs are met.
Signs of an Anxious Dog
Understanding the emotional state of your dog is crucial for ensuring their well-being and happiness. Anxiety in dogs can manifest in various forms, and recognizing the signs of an anxious dog is essential for timely intervention. One of the most common indicators is excessive barking, which can emerge as a response to discomfort or stress. While occasional barking is normal, persistent barking could signal underlying anxiety.
Another significant sign of anxiety is hiding behavior. An anxious dog may seek refuge in corners, under furniture or in closed spaces, indicating a desire to escape from perceived threats. Likewise, trembling or shivering can be seen in anxious dogs, especially during stressful situations such as thunderstorms or fireworks. It’s vital to observe these behaviors closely, as they often serve as primary indicators of your dog’s emotional health.
Changes in appetite also signal anxiety in dogs. A once enthusiastic eater may lose interest in food when feeling anxious, leading to potential health issues if not addressed. Additionally, the physiological responses of anxious dogs are noteworthy; panting and pacing are not merely signs of excitement but can reflect a state of distress. This restlessness may occur even in the absence of physical exercise, highlighting their emotional turmoil.
Recognizing these signs early is paramount to preventing further behavioral issues, as unchecked anxiety can escalate into more severe conditions. Common triggers include loud noises, changes in routine, or alterations in their environment, such as moving to a new home. Being vigilant about your dog’s reactions and emotions will help ensure that they receive the necessary support to overcome their anxiety, fostering a harmonious relationship between you and your furry companion.
Comparative Analysis: Happiness vs. Anxiety
Understanding the emotional states of dogs is crucial for pet owners. Happiness and anxiety can manifest similarly in dogs, yet each state has distinct signs that reflect a dog’s well-being or distress. Recognizing these differences enables pet owners to respond appropriately to their pets’ needs.
When a dog is happy, its body language is open and relaxed. Signs of happiness include a wagging tail, often held high and moving in a broad arc. The dog may exhibit a playful demeanor, with barks that are enthusiastic rather than sharp or urgent. Moreover, happy dogs exhibit soft, relaxed facial expressions, including a slightly open mouth, which can appear as a ‘smile.’ They may also engage in playful actions, such as bowing or inviting play with their owners or other dogs.
Conversely, anxiety in dogs typically manifests through more rigid body language. A dog experiencing anxiety may tuck its tail between its legs, keep its ears pulled back, or display avoidance behavior, such as hiding or backing away. Vocalizations associated with anxiety include whines, whimpers, or barking that appears frantic or repetitive. The dog’s facial expression may reflect distress, with narrowed eyes, a closed mouth, and excessive licking of the lips. Physical manifestations of anxiety can also include trembling or pacing, illustrating the dog’s unease.
It is essential for pet owners to correctly interpret these signals. Context is critical; a dog that is wagging its tail while playing may be happy, but a dog wagging its tail in a stiff manner may be signaling anxiety or uncertainty. Additionally, recognizing these behaviors can facilitate effective training techniques and foster emotional well-being. Understanding the nuanced differences between happiness and anxiety can significantly impact the relationship owners have with their dogs, ensuring that both the pet and the owner thrive in a harmonious environment.
How to Ensure Your Dog’s Emotional Well-Being
Ensuring your dog’s emotional well-being is vital for fostering happiness and alleviating anxiety. One of the primary steps in this endeavor is to create a stimulating environment that encourages exploration and play. Providing your dog with various toys, puzzles, and spaces to explore can enrich their daily life and stimulate their cognitive abilities. This not only keeps them engaged but also helps to mitigate boredom-related anxiety.
Regular exercise and play are equally crucial components in promoting emotional well-being. Activities that involve physical exertion, such as walking, jogging, or playing fetch, should be incorporated into your dog’s daily routine. Exercise not only promotes physical health but also releases endorphins that can elevate mood and reduce stress levels in dogs. Engaging in play with your dog, whether through games or interactive toys, creates a positive bond that reinforces their sense of security.
Establishing a consistent routine can further contribute to your dog’s emotional stability. Animals thrive on predictability, and knowing when to expect meals, walks, and playtime can minimize anxiety. Routine provides a structure that can help reduce stress and build comfort, allowing your dog to feel secure in their environment.
In certain cases, seeking professional help may be necessary. Consulting with a veterinarian or a certified dog trainer can provide insights into behavioral issues and anxiety management techniques. They can assist in addressing specific challenges your dog may face, ensuring their emotional health is prioritized.
Positive reinforcement during training sessions not only improves behavior but also enhances the bond between you and your dog. This method encourages learning through reward-based systems, promoting a sense of achievement in your pet. Additionally, proper socialization with other dogs and people can further cultivate a sense of happiness, helping your dog to become more adaptable and confident. Ultimately, a balanced lifestyle comprising physical, mental, and social stimulation is key to ensuring your dog leads a fulfilling and emotionally healthy life.